 Alone atop the standings of those seeking U.S. patents is the International Business Machines Corporation (NYSE:IBM) of Armonk, NY, a multinational technology and consulting corporation that markets a wide range of computing hardware and software solutions.
Alone atop the standings of those seeking U.S. patents is the International Business Machines Corporation (NYSE:IBM) of Armonk, NY, a multinational technology and consulting corporation that markets a wide range of computing hardware and software solutions.
During 2014, IBM broke its own record for the greatest number of U.S. patents granted by the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office with 7,534 patents granted during that time. This makes the 22nd consecutive year that IBM has been the top patent earner at the PTO. According to the company’s fourth quarter earnings report for fiscal year 2014, IBM invested about six percent of its revenues into research and development during 2014; we’ve seen other companies like Microsoft invest as much as 12 percent of revenue into R&D. IBM is active in protecting its IP holdings and recently filed suit against Priceline Group and others who were infringing patents in online technologies issued to IBM in the late 1990s.
Poor demand in the software industry is just one reason why IBM’s revenues dropped by two percent year-over-year in 2014’s fourth quarter, down to a total of $24.1 billion. IBM’s global workforce also dwindled last year by more than 51,000 workers, a decline of 12 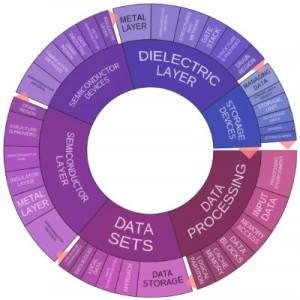 percent to a total of 379,592 employees by the year’s end. IBM is still investing in its Watson cloud-based data analytics platform and recently spent an unspecified amount to acquire AlchemyAPI, a deep learning start-up with a community of 40,000 developers.
percent to a total of 379,592 employees by the year’s end. IBM is still investing in its Watson cloud-based data analytics platform and recently spent an unspecified amount to acquire AlchemyAPI, a deep learning start-up with a community of 40,000 developers.
Patenting activities continue to move forward at IBM at a blistering pace. According to our research with Innography’s patent portfolio analysis tools, the corporation earned 1,745 patents from the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office during a recent three-month period. Over a year, that would total 6,980 patents, a slight drop from last year’s totals but still well ahead of 2nd-place Samsung’s 2014 results, and there is still plenty of time for IBM to continue to best their own record, which is something they seem to continually do year after year. As the text cluster posted here shows us, much of IBM’s recent patents are focused on data sets and processing, indicating progress in its data analytics development programs, while semiconductors are also very important to the company’s IP portfolio in the past few months.
[Companies-1]
IBM’s Technology Spurs Better Data Analysis for Organizations
Improved data analytics and the more intelligent use of data for business purposes has been a great focus among the products and services that IBM has been marketing recently. Much of this focus has been supported by the corporation’s belief that data analytics and related services will become a $40 billion per year business for IBM by 2018.
A trio of patents issued to this corporation in recent weeks reflects some of this work. We were intrigued by the journalistic integrity that IBM is seeking to support with the technology disclosed by U.S. Patent No. 8972321, which is titled Fact Checking Using and Aiding Probabilistic Question Answering. The patent protects a method of verifying a statement by receiving a statement at a first computing system, decomposing the received statement into sets of question and answer pairs, determining a confidence value of each answer in the question and answer sets and combining the determined confidence values to generate a probability that the received statement is correct. This system obviates the need to manually fact check of a statement before it is published; the patent’s background section cites the fact that some newspaper organizations maintain up to 80 full-time employees just for fact checking purposes. The extraction of more valuable and meaningful data information from the data collected by a business entity is the focus of U.S. Patent No. 8965895, issued under the title Relationship Discovery in Business Analytics. The computer system disclosed here includes a processor which executes instructions to perform operations involving the processing of (k-1) dimensional tables with the use of goodness of fit value statistics that evaluate model capability to describe data. This invention provides a cloud-based service for defining, executing and extracting valuable information from a statistical analysis, especially when dealing with large data sets that are problematic for individuals to parse effectively. More effective methods of searching for physic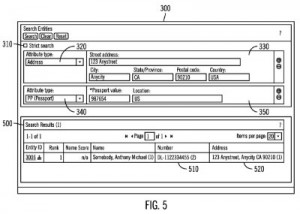 al entities of any kind, from buildings to people to small objects, are discussed within U.S. Patent No. 8972387, issued under the title Smarter Search. The method to search for an entity in an entity resolution system claimed here involves receiving search input made up of attributes, performing a resolution search using the search input to generate a first search result set of entities based on similarities between the search input and the entities, determining that the resolution search generated at least two generic attributes and performing a query search to identify additional entities based on the generic attributes to generate a second search result set. This innovation provides some automated refining of searches so that individuals can more easily information related to specific entities.
al entities of any kind, from buildings to people to small objects, are discussed within U.S. Patent No. 8972387, issued under the title Smarter Search. The method to search for an entity in an entity resolution system claimed here involves receiving search input made up of attributes, performing a resolution search using the search input to generate a first search result set of entities based on similarities between the search input and the entities, determining that the resolution search generated at least two generic attributes and performing a query search to identify additional entities based on the generic attributes to generate a second search result set. This innovation provides some automated refining of searches so that individuals can more easily information related to specific entities.
IBM Develops Intriguing Upgrades for Digital Book Content
Interestingly enough, we came across a couple of patents issued recently for technologies related to digital content such as e-books and audiobooks. A gesture technology developed for use in e-books to make the reading experience feel more like the physical experience of reading a book is described by U.S. Patent No. 8966391, entitled Force-Based Contextualizing of Multiple Pages for Electronic Book Reader. The patent discloses a method for contextualizing a page turn in an electronic book corresponding to an amount of force applied by a user in a snap gesture triggering the page turn performed by an e-reader program running in a tablet device. This invention allows an e-book reader to flip through a number of sequential pages with a simple gesture, much like could be accomplished 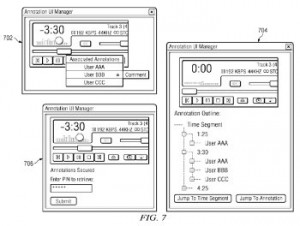 with a paperback or hardcover book. A tool that allows an audiobook listener to make notes on a chapter or a certain portion of text is outlined within U.S. Patent No. 8973153, which is titled Creating Audio-Based Annotations for Audiobooks. The patent protects a method for publishing an audible annotation to an audio signal by recording a human’s audible annotation to the audio signal and electronically storing the annotation for access by a social networking host computer, receiving a request at the social networking host computer by a different human to audibly render the signal with the annotation and identifying whether the second human user has a license to view the audio signal. This system would be useful for making annotations while performing research with audiobooks or simply for sharing insights with others who may be consuming the same content.
with a paperback or hardcover book. A tool that allows an audiobook listener to make notes on a chapter or a certain portion of text is outlined within U.S. Patent No. 8973153, which is titled Creating Audio-Based Annotations for Audiobooks. The patent protects a method for publishing an audible annotation to an audio signal by recording a human’s audible annotation to the audio signal and electronically storing the annotation for access by a social networking host computer, receiving a request at the social networking host computer by a different human to audibly render the signal with the annotation and identifying whether the second human user has a license to view the audio signal. This system would be useful for making annotations while performing research with audiobooks or simply for sharing insights with others who may be consuming the same content.
IBM Continues to Build a Richer Virtual Universe
In our most recent coverage of IBM in the Companies We Follow series, we noted that there were some interesting developments at the company in the field of virtual universes. We found another pair of patents related to these expansive digital worlds during our latest survey of IBM’s patented technologies. A system for ensuring that the highest number of objects contained within a three-dimensional scene are seen by a person navigating the scene is the focus of U.S. Patent No. 8970586, which is titled Building Controllable Clairvoyance Device in Virtual World. The patent claims a clairvoyance method for a 3D scene by acquiring parameters associated with a clairvoyance camera and a clairvoyance viewport, determining a 3D scene to be rendered according to those parameters, rendering the 3D scene to obtain a 2D image presented in the clairvoyance viewport and composing the 2D image presented in both a clairvoyance viewpoint and a general scene viewport. This system overcomes issues of inconvenient manipulation 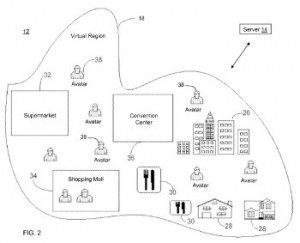 and low efficiency in modifying a 3D scene view to uncover an object. Techniques to handle the enormous amounts of data processing required to present these complex 3D virtual worlds are disclosed by U.S. Patent No. 8972870, entitled Providing Alternative Representations of Virtual Content in a Virtual Universe. The patent protects a method for automatically reducing load on a server functioning with a virtual universe by detecting a load on the server, determining whether the load exceeds a predefined threshold and annotating a definition of a virtual reality modeling language with metadata to automatically generate an alternative representation of a virtual content to reduce a load on the server if it’s detected that the load exceeds the threshold. This system is designed to handle data loads more efficiently in virtual universes which cater to a million or more avatars.
and low efficiency in modifying a 3D scene view to uncover an object. Techniques to handle the enormous amounts of data processing required to present these complex 3D virtual worlds are disclosed by U.S. Patent No. 8972870, entitled Providing Alternative Representations of Virtual Content in a Virtual Universe. The patent protects a method for automatically reducing load on a server functioning with a virtual universe by detecting a load on the server, determining whether the load exceeds a predefined threshold and annotating a definition of a virtual reality modeling language with metadata to automatically generate an alternative representation of a virtual content to reduce a load on the server if it’s detected that the load exceeds the threshold. This system is designed to handle data loads more efficiently in virtual universes which cater to a million or more avatars.
Medical and Fitness Innovations Pursued at IBM
IBM has some very unique plans on how to utilize its data analytics platforms in order to provide medical and healthcare solutions that would affect a wide array of people. For example, IBM is attempting to harness its Watson data analytics platform to perform genomic analysis on a person’s DNA to inform fitness goals, such as how long or far a person can safely jog at their current elevation. The analysis of physiological data to determine the medical resources that a patient needs is featured within U.S. Patent No. 8968197, which is titled Directing a User to a Medical Resource. It claims a computer program product for directing a user to a medical resource, the program performing a method of determining a real-time state of a user’s medical condition based on physiological sensor readings and correlating that real-time state to a medical resource. This system is designed to send directions to a user suffering from an acute medical condition to the closest medical resource, even a temporal resource, that has the capability of ameliorating a condition.
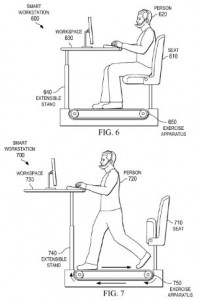 We also found an intriguing innovation designed to bring a person’s exercise routine into the workplace, as is evidenced in U.S. Patent No. 8965541, issued under the title Exercise-Integrated Workstation. The patent claims a method for initiating an exercise sequence of an exercise equipment communicatively coupled to a computer processor by identifying a set of monitored activities running in the processor, identifying a set of preferences and goals for the exercise sequence, identifying a set of details regarding user modifications to previous exercise sequences and determining whether to initiate the exercise sequence based on these data sets and any scheduled events that might interfere. The invention is intended to allow business professionals to find time to work an exercise routine into their schedules despite how busy they are.
We also found an intriguing innovation designed to bring a person’s exercise routine into the workplace, as is evidenced in U.S. Patent No. 8965541, issued under the title Exercise-Integrated Workstation. The patent claims a method for initiating an exercise sequence of an exercise equipment communicatively coupled to a computer processor by identifying a set of monitored activities running in the processor, identifying a set of preferences and goals for the exercise sequence, identifying a set of details regarding user modifications to previous exercise sequences and determining whether to initiate the exercise sequence based on these data sets and any scheduled events that might interfere. The invention is intended to allow business professionals to find time to work an exercise routine into their schedules despite how busy they are.
Other IBM Patents: Vehicle Fuel Efficiency and Removing Sports Broadcaster Audio
We’ll close out our survey of the recent additions to IBM’s patent portfolio with a look at a few technologies that were very interesting, even if they didn’t fit any of the other areas of innovation that we’ve covered today. We’ve been talking a lot this year about automobile innovations from all over the world so we were intrigued to learn about an IBM patent for a vehicular technology, as is reflected by U.S. Patent No. 8972163, which is titled Vehicle Fuel Efficiency Optimization Based on Vehicle Usage Patterns. This patent protects a method for indicating vehicle fuel efficiency for at least one vehicle usage pattern by analyzing a set of usage patterns for a vehicle, calculating a vehicle fuel efficiency for each of the vehicle usage patterns and providing a real-time notification to a vehicle user indicating calculated fuel efficiency as well as the monetary value sacrificed by a usage pattern that contributes to inefficient fuel consumption.
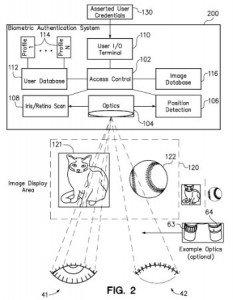 Security procedures that require a person to undergo an eye scan in order to be authenticated are disclosed by U.S. Patent No. 8953851, which is titled Ocular Biometric Authentication with System Verification. The biometric user authentication method claimed here involves receiving asserted user credentials into a biometric authentication system, obtaining a digitally-stored image key and ocular biometric data which are both associated with the user credentials, displaying the image key in view of one eye, detecting that the user has selected the image key by closing his or her opposite eye, authenticating a user by scanning the open eye and providing a user with access to a protected area in response to verifying the user. This system addresses shortcomings in both retina scans, which can be uncomfortable to a person, used in high-traffic screening situations.
Security procedures that require a person to undergo an eye scan in order to be authenticated are disclosed by U.S. Patent No. 8953851, which is titled Ocular Biometric Authentication with System Verification. The biometric user authentication method claimed here involves receiving asserted user credentials into a biometric authentication system, obtaining a digitally-stored image key and ocular biometric data which are both associated with the user credentials, displaying the image key in view of one eye, detecting that the user has selected the image key by closing his or her opposite eye, authenticating a user by scanning the open eye and providing a user with access to a protected area in response to verifying the user. This system addresses shortcomings in both retina scans, which can be uncomfortable to a person, used in high-traffic screening situations.
Sports fans who think that the play-by-play and color commentary just gets in the way of the broadcast should be ready to cheer for the technology explained within U.S. Patent No. 8965181, entitled Automatic Announcer Voice Attenuation in a Presentation of a Broadcast Event. The patent protects a method performed in a computer system of dividing an audio input signal of a broadcast event into a plurality of audio segments, some of which include both crowd noise and announcer commentary, separating the segments based on whether the amplitude of the crowd noise or announcer commentary is greater, storing them in respective libraries, generating an attenuated version of an audio segment and outputting blended audio output signals in a chronological order. This system of removing announcer commentary from sports broadcasts does not require the use of specialized recording methods.

![[IPWatchdog Logo]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/themes/IPWatchdog%20-%202023/assets/images/temp/logo-small@2x.png)

![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Artificial-Intelligence-2024-REPLAY-sidebar-700x500-corrected.jpg)
![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/UnitedLex-May-2-2024-sidebar-700x500-1.jpg)
![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Patent-Litigation-Masters-2024-sidebar-700x500-1.jpg)

![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/WEBINAR-336-x-280-px.png)
![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/2021-Patent-Practice-on-Demand-recorded-Feb-2021-336-x-280.jpg)
![[Advertisement]](https://ipwatchdog.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Ad-4-The-Invent-Patent-System™.png)






Join the Discussion
One comment so far.